
Genotoxicity Tests
Genotoxicity /Genotoxicity--ISO 10993-3, GB/T 16886.3, YY/T 0127, OECD
Genotoxicity refers to the ability to kill cell DNA directly or indirectly. For example, benzopyrene in cigarette smoke is genotoxic. These compounds are mutagenic and alter proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.



Introduction of Genotoxicity Tests
Genotoxicity refers to the ability to kill cell DNA directly or indirectly. For example, benzopyrene in cigarette smoke is genotoxic. These compounds are mutagenic and alter proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.
Application of standard:
ISO 10993-3, GB/T 16886.3, OECD471, OECD473, OECD474, OECD476, YY/T 0127
Test Method and Principle
Ames test (Salmonella typhimurium revert mutation test) |
Histidine trophic deficiency (His -) strain of Salmonella typhimurium can only divide a few times in medium containing a trace amount of histidine, except for a very few cells that spontaneously revert to mutations, forming microscopic colonies. After being treated by the mutagens, a large number of cells revert to mutation, synthesize histidine by themselves, and develop into visible colonies. Count the number of regressive colonies on the lowest trophic plate to determine whether the subject is mutagenic. Some chemicals need to be metabolically activated to have mutagenic effects. Adding mammalian microsomal enzymes in the test system can make up for the lack of metabolic activation system in vitro test. |
Mammalian cells in vitro Gene mutation test |
Thymidine kinase, a product of the TK gene, catalyzes the production of thymidine monophosphate (TMP) from deoxythymidine (TDR) in vivo. Under normal circumstances, this reaction is not necessary for life because the majority of TMP in the body comes from deoxyuracil nucleotide (dUMP), which is a dUMP methylation reaction catalyzed by thymidylate synthase to produce TMP. However, when a thymidine analogue (TFT-trifluorothymidine) is added to the cell culture, the TFT, catalyzed by thymidine kinase, can produce trifluorothymidine, which is then incorporated into DNA, resulting in lethal mutations, and the cell cannot survive. If TK gene mutation leads to thymidine kinase deficiency, TFT cannot be phosphorylated, nor can it be incorporated into DNA, so cells can grow in medium containing TFT, that is, they show resistance to TFT. According to the number of mutant colonies, the mutation frequency was calculated to determine the mutagenicity of the tested species.TK gene mutation test can detect a variety of genetic changes, including point mutations, large deletions, recombination, chromosomal aneuploidy, and other large-scale genomic changes. The target cell lines used in the experiment mainly included mouse lymphoma cells L5178Y. The test sample is considered positive when the mutation frequency is dose-dependent, which is twice or more than that of the negative control. |
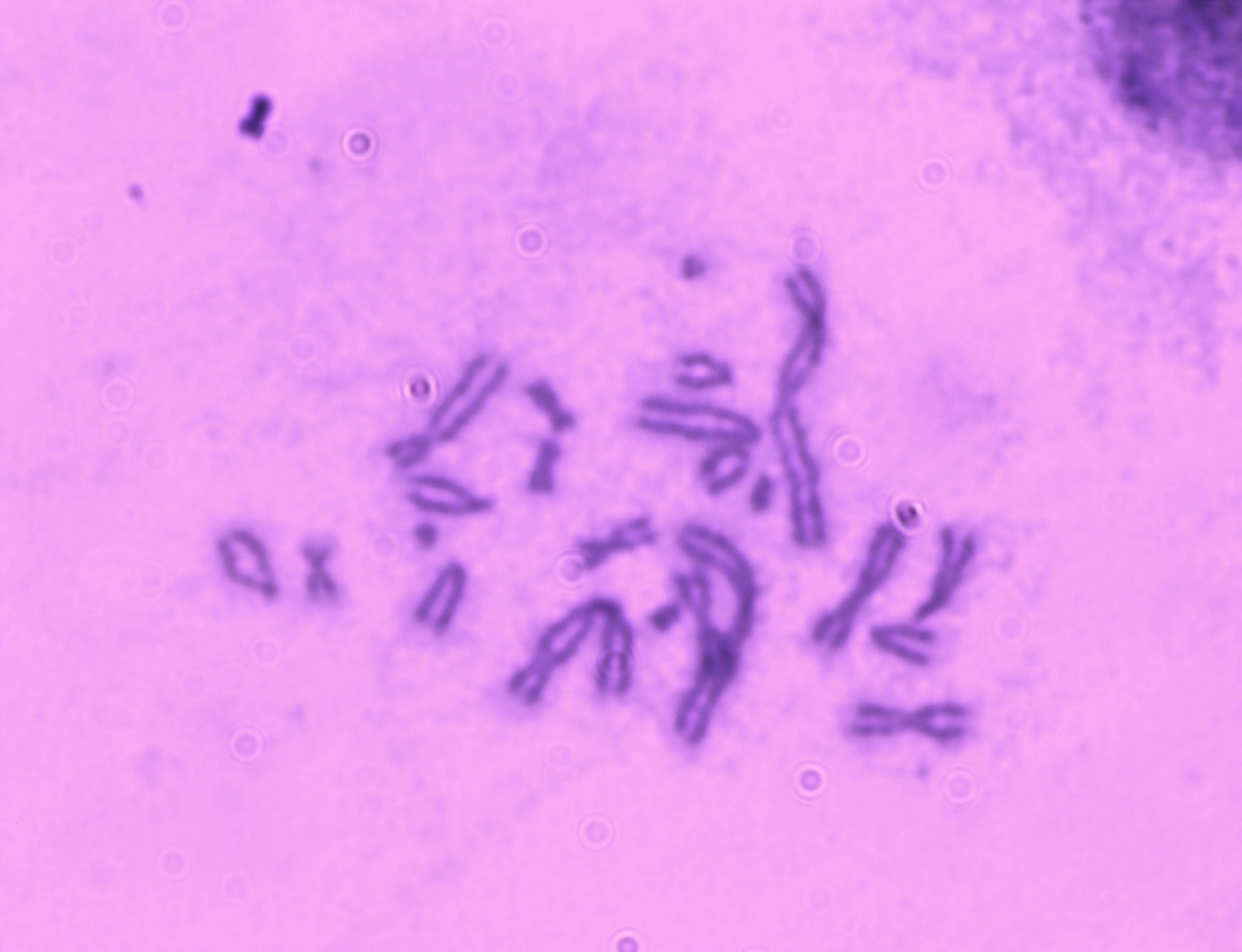
Chromosome aberration test |
The peripheral blood lymphocytes or human and mammalian somatic cell lines can be used as materials. The commonly used somatic cell lines include Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO), Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts (V79 and CHL), and human embryonic lung diploid fibroblasts. Chromosomal aberrations can be divided into chromosome structural aberrations and number aberrations. Chromosomal structural aberrations can be divided into fissure, deletion, short film and interchange. After joining and not join the metabolic activation system under the condition of the cultured mammalian cells exposed to objects, subjects with middle blockers split phase (such as colchicine or colchicine) treatment, make the cell stops in the middle of split phase, then harvest cells, production, dyeing, microscope analysis of chromosome aberration distortion type, cell distortion, total structure aberration rate. In vitro experiments are often more sensitive than in vivo experiments because the subject is in direct contact with cells. |
Micronucleus Test |
Micronuclei are chromatids or acentric segments or rings of chromosomes that remain in the cytoplasm when chromosomes regularly enter into daughter cells to form nuclei in the late stage of mitosis. After the terminal stage, it forms one or several regular subnuclei alone, which are contained in the cytoplasm of the cell. Because it is much smaller than the nucleus, it is called micronucleus. |
Period
The test period is 8~10 weeks. Please contact Epintek for details.
Sample Request(Single Polor)
Method | Number | The sample thickness(<0.5 mm) | The sample thickness(>0.5 mm) | weight |
Ames test | 2 | 30 cm2 | 15 cm2 | 1g |
Gene mutation test | 2 | 400 cm2 | 200 cm2 | 13g |
Chromosome aberration test | 2 | 400 cm2 | 200 cm2 | 13g |
Micronucleus Test | 2 | 240 cm2 | 120 cm2 | 8 g |
Copyright © EPINTEK GROUP
Powerd by PEERHI
EPINTEK GROUP
Tel: +86 21 54736833
Address: 4th Floor, T2 Wanjin Center, Lane 360, Xinlong Road, Minhang District, Shanghai
E-mail: stefanie.sun@epintek.com




We Focus on the Demand for Innovation
